In this post, you’ll learn about the complexities of keeping the deployment train running.

Last week I spoke to a few of my Wikimedia Foundation (WMF) colleagues about how we deploy code—I completely botched it. I got too complex too fast. It only hit me later—to explain deployments, I need to start with a lie.
M. Jagadesh Kumar explains:
“Every day, I am faced with the dilemma of explaining some complex phenomena […] To realize my goal, I tell ‘lies to students.’”
This idea comes from Terry Pratchett’s “lies-to-children” — a false statement that leads to a more accurate explanation. Asymptotically approaching truth via approximation.
Every section of this post is a subtle lie but approximately correct.
Release Train
The first lie I need to tell is that we deploy code once a week.
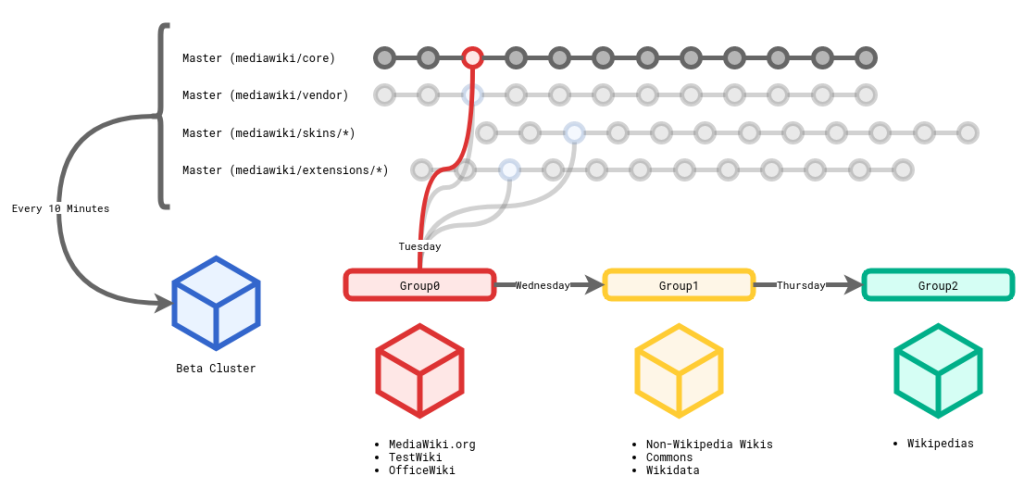
Every Thursday, Wikimedia Release Engineering Team deploys a MediaWiki release to all 978 wikis. The “release branch” is 198 different branches—one branch each for mediawiki/core, mediawiki/vendor, 188 MediaWiki extensions, and eight skins—that get bundled up via git submodule.
Progressive rollout
The next lie gets a bit closer to the truth: we don’t deploy on Thursday; we deploy Tuesday through Thursday.
The cleverly named TrainBranchBot creates a weekly train branch at 2 am UTC every Tuesday.
- Tuesday
- Deploy to Group0—132 wikis, including Test Wikipedia, mediawiki.org, and Office wiki (our internal WMF MediaWiki)
- Wednesday
- Deploy to Group1—528 wikis, including Commons and Wikidata. Most non-Wikipedia wikis (plus Catalan Wikipedia and Hebrew Wikipedia)
- Thursday
- Deploy to remaining 320 wikis, including our largest wiki: English Wikipedia
Progressive rollouts give users time to spot bugs. We have an experienced user-base—as Risker attested on the Wikitech-l mailing list:
“It’s not always possible for even the best developer and the best testing systems to catch an issue that will be spotted by a hands-on user, several of whom are much more familiar with the purpose, expected outcomes and change impact on extensions than the people who have written them or QA’d them.”
Bugs
Now I’m nearing the complete truth: we deploy every day except for Fridays.
Brace yourself: we don’t write perfect software. When we find serious bugs, they block the release train — we will not progress from Group1 to Group2 (for example) until we fix the blocking issue. We fix the blocking issue by backporting a patch to the release branch. If there’s a bug in this release, we patch that bug in our mainline branch, then git cherry-pick that patch onto our release branch and deploy that code.
We deploy backports three times a day during backport deployment windows. In addition to backports, developers may opt to deploy new configurations or enable/disable features in the backport deployment windows
Release engineers train others to deploy backports twice a week.
Emergencies
We deploy on Fridays when there are major issues. Examples of major issues are:
- Security issues
- Data loss or corruption
- Availability of service
- Preventing abuse
- Major loss of functionality/visible breakage
We avoid deploying on Fridays because we have a small team of people to respond to incidents. We want those people to be away from computers on the weekends (if they want to be), not responding to emergencies.
Non-MediaWiki code
There are 42 microservices on Kubernetes deployed via helm. And there are 64 microservices running on bare metal. The service owners deploy those microservices outside of the train process.
We coordinate deployments on our deployment calendar wiki page.
The whole truth
We progressively deploy a large bundle of MediaWiki patches (between 150 and 950) every week. There are 12 backport windows a week where developers can add new features, fix bugs, or deploy new configurations. There are microservices deployed by developers at their own pace.
Important Resources:
More resources:
Thanks to @brennen, @greg, @KSiebert, @Risker, and @VPuffetMichel for reading early drafts of this post. The feedback was very helpful. Stay tuned for “How we deploy code: Part II.”
About this post
This post originally appeared in the Phame blog, “Doing the Needful,” on 27 Sept 2021 and the Wikimedia Techblog on 28 September, 2021

Can you help us translate this article?
In order for this article to reach as many people as possible we would like your help. Can you translate this article to get the message out?
Start translation